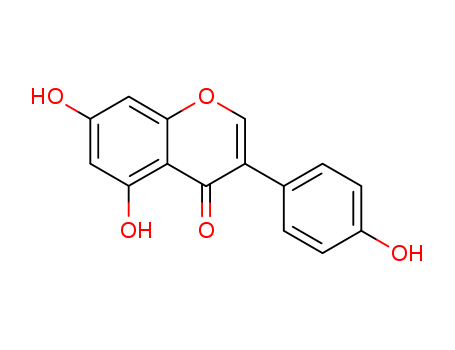
Genistein CAS NO.446-72-0
- FOB Price: USD: 150.00-290.00 /Kilogram Get Latest Price
- Min.Order: 50 Kilogram
- Payment Terms: L/C|D/A|T/T|Westem Union|
- Product Details
Keywords
Quick Details
- ProName: Genistein
- CasNo: 446-72-0
- Molecular Formula: C15H10O5
- Appearance: Light yellow crystal powder
- Application: Genistein is a tyrosine-specific inhib...
- DeliveryTime: within 3-5 days
- PackAge: Packed in paper-drums and two plastic-...
- Port: Xiamen
- ProductionCapacity: 2000 Kilogram/Week
- Purity: NLT98% HPLC
- Storage: Store in cool & dry place. Keep away f...
- LimitNum: 50 Kilogram
Superiority
Standardized Genistein powder.
Botanical Source:Genista tinctoria Linn, Sophora subprostrala Chun et T.Chen
Appearance: L…
Details
Standardized Genistein powder.
Botanical Source:Genista tinctoria Linn, Sophora subprostrala Chun et T.Chen
Appearance: Light yellow crystal powder
Standard Concentrate ratio: NLT98% HPLC
Package: 25/KG per paper drum or packed with little parcel.
Sample/ COA / MSDS are available
Functions;
1. Genistein is an isoflavonoid phytoestrogenic compound found in soybeans, pea pods, and other legumes. The estimated human normal dietary intake of genistein, primarily as glycosides, is 0 to 0.5 mg/kg. Genistein is present in much greater amounts in nutritional supplements.
2. Genistein is carcinogenic in female neonatal mice, inducing endocrine-dependent uterine tumors in a fashion similar to diethylstilbestrol (DES).
3. Genistein is a tyrosine-specific inhibitor of protein kinase activity, blocking the tyrosine-phosphorylation of histone H2B. In adult animals, dietary genistein has chemopreventive effects on breast, prostate, and other endocrine-dependent tumors.
4. Genistein acts as an antioxidant, similar to many other isoflavones, counteracting damaging effects of free radicals in tissues
5. Genistein protects against pro-inflammatory factor-induced vascular endothelial barrier dysfunction and inhibits leukocyte-endothelium interaction, thereby modulating vascular inflammation, a major event in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis